Table of Contents
What is Threat Hunting?
Threat hunting involves proactively searching for advanced and persistent threats that may have evaded traditional security measures within the network. Threat hunters actively seek out contacts with indicators of compromise (IOCs) and other suspicious activity within their network. The primary objective of threat hunting is to detect and mitigate threats before they cause significant damage or exfiltrate sensitive information.
Though it sounds like a straightforward concept, threat hunting typically requires skilled cybersecurity professionals who have a deep understanding of both the organization’s environment and the current threat landscape.
Effective threat hunting involves a blend of human ingenuity and tools. Defensive tools rely on rules, heuristics, and outliers but cannot emulate human cybersecurity practitioners’ creativity. Cybersecurity tools need to empower threat hunters by automating simpler tasks and allowing them to apply their human ingenuity where it is most valuable. Threat hunters are also empowered by having relevant contextual information at their fingertips.
With the right empowering tools, threat hunting is not just reserved for only the most elite cybersecurity operators. Technology can empower any organization to mature its cybersecurity operations by adopting a threat-hunting practice.
The Pyramid of Pain
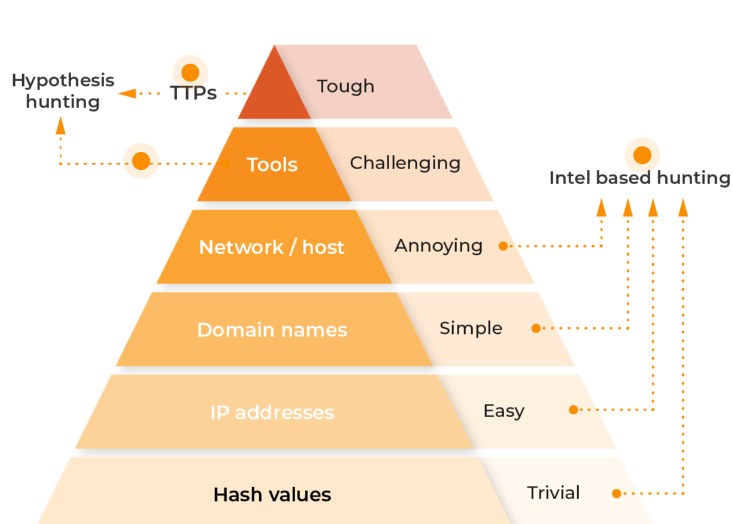
Most threat hunters are likely familiar with the Pyramid of Pain, developed by security researcher David J. Bianco. The Pyramid of Pain is essentially a hierarchy that shows how difficult it is for cybersecurity professionals to make the attackers’ lives harder.
Each step of the pyramid is important, but the goal for cybersecurity professionals is to conquer the top layers of the pyramid. Disrupting attackers at this level makes it much more difficult for them to achieve their goals.
How Lumu Helps
Lumu eases the ‘pain’ associated with this process and enables cybersecurity professionals to get insights into even the most intricate details addressing every level of the pyramid from top to bottom.
Lumu’s Illumination Process is responsible for automatically and continuously hunting for threats that are active on the network. The process starts by ingesting network metadata—DNS, network flows, firewall logs, proxy logs, and email data. This network metadata is correlated against known IoCs while a machine learning algorithm detects anomalous activity and feeds it through a deep correlation phase that delivers only malicious incidents of high probability.
With our ability to collect and analyze data in real time, we’re constantly identifying IoCs and classifying malicious activity discovered across our customer base. Every IoC discovered creates a new incident (although related IoCs are grouped into a singular incident), and this triggers an automated threat-hunting exercise.
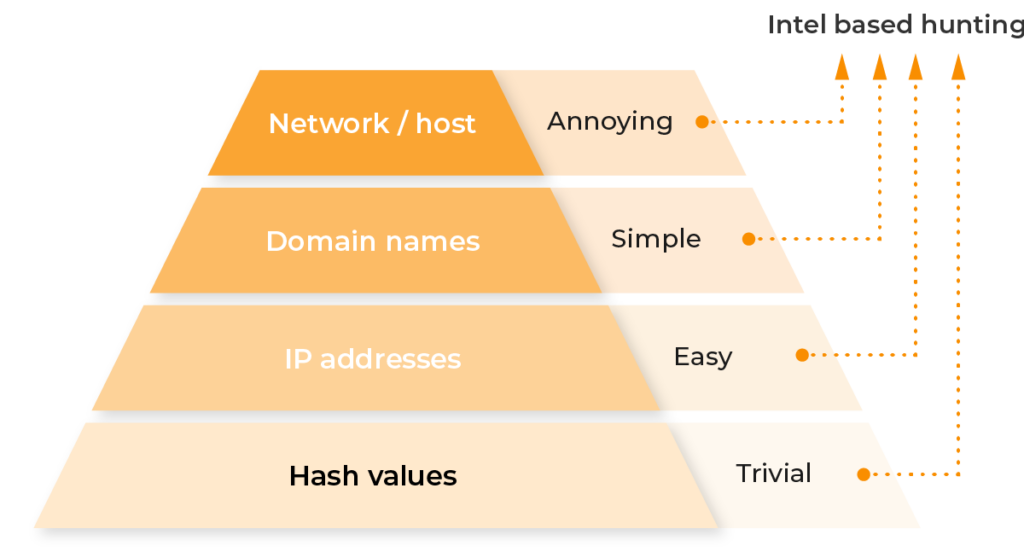
All Lumu incidents contain data around Intel-based Hunting, which provides all associated hash values, IP addresses, domain names, and network information. Armed with this information, hunters don’t need to conduct tedious exercises to obtain the necessary threat intelligence which allows them to respond and mitigate threats quickly or develop additional hypotheses to test through hunting excercises.
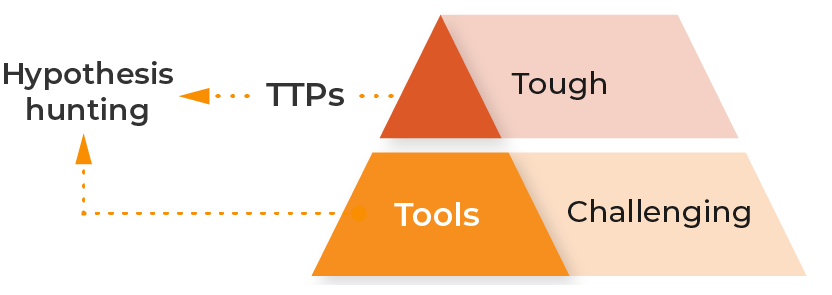
Focusing on the top two steps of the pyramid is essential for proactive defense and response strategies. Lumu helps in this area by providing insights into the long-term objectives and goals of attackers. TTPs and Tools are the hardest for attackers to change since they represent their core mission. Through our incident context organizations can instantly see the tactics and techniques attackers are using to target them.
Every incident provides threat hunters with deep context into the attack type and assets in the organization that continue to be targeted. Additionally, MITRE ATT&CK Matrix™ mapping within incidents shows exactly how adversaries are targeting organizations. Disrupting attackers at this level makes it much more difficult for them to achieve their goals.
Where to Begin
The threat hunting practice involves a three-step process and Lumu empowers threat hunters each step of the way.
Trigger: The trigger is an event or observation that initiates the threat hunting process.
How Lumu Helps:
- Incidents: Provides coordinates and information from endpoints to trigger your threat hunting exercise.
- Playback: Lumu stores two years of metadata and compares prior metadata with new threat intelligence to defend against zero-day threats and emerging attacks. Each new IoC automatically prompts a retrospective hunting exercise.
- Global Mitre Matrix: Gives a detailed view of the tactics and techniques attackers are using to target your organization to prioritize threat hunting and red team exercises.
Investigation: After the trigger is identified, threat hunters start the investigation phase. At this point, they will gather as much context and information as they can.
- Threat Triggers: Contains Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) related to an incident as reported by Lumu’s threat intelligence engines or third-party sources.
- Compromise Radar: Shows threat hunters contact patterns to help distinguish occasional contact from persistent and automated attacks.
- Attack Distribution: Enables prioritization by uncovering which areas of the organization are most affected by threat actors.
Resolution: The resolution phase involves taking actions against threats which includes containment measures to stop the threat.
How Lumu helps:
- Operational Timeline: All incidents contain a timeline section where teams can track the steps of the resolution flow.
- Email Reports: Each incident provides the ability to email all of the details of what happened and what actions were taken directly to your CISO and others as needed.
- Response Automation: Hunters can connect Lumu with their existing cyber stack to take automated actions against active threats.
Our goal has always been to simplify cybersecurity so that anyone can operate it. We tailor our technology to be user friendly and easy to operate, helping security teams be more efficient through our tools and features.
To learn more about Lumu for threat hunting, click here.