The MOVEit vulnerability stands out as a zero-day threat currently being exploited by the CL0P Ransomware Group and others. While numerous zero-day vulnerabilities lurk in the shadows of our digital environments, this one has stepped into the spotlight for causing significant breaches in large and critical enterprises including software firms high up in the supply chain. The escalating exploitation of this vulnerability underscores its significance, compelling organizations to take swift, robust action in response.
What Is the MOVEit Vulnerability?
This vulnerability, categorized as CVE-2023-34362 by MITRE, is a recent discovery in the MOVEit software. MOVEit is designed to facilitate secure file and data transfers. Unfortunately, it harbors a SQL injection vulnerability that is highly exploitable and undermines the very security it was intended to provide.
The risk from this vulnerability is significant, with a criticality rating of 9.8 according to MITRE. Attackers who exploit it can execute arbitrary code, escalate privileges, and insert ransomware. In some instances, the inclusion of a file named ‘human2.aspx’ was observed to generate persistence.
On June 7th, 2023, CISA alongside the FBI released a joint advisory announcing that the Cl0p Ransomware Group was actively exploiting this vulnerability.
Furthermore, a second (CVE-2023-35036) and third (CVE-2023-35708) MOVEit vulnerability was later discovered. These vulnerabilities can also lead to privilege escalation, but at the time of writing, their severity is uncertain.
Who Is Affected by the MOVEit Vulnerability?
According to the CL0P Ransomware Group, this is an ‘exceptional’ exploit that has reportedly been used to compromise hundreds of companies, including banks, universities, and multinationals. The exploit has also been linked to recent attacks on various federal agencies, including energy sector entities.
In the following wave of attacks, the following U.S. entities have been compromised by CL0P Ransomware, according to CL0P’s own leaks website: Colorado Department of Health Care Policy & Financing, University of Rochester, Minnesota Department of Education, Oregon Department of Transportation (ODOT), U.S. Department of Agriculture, United States Office of Personnel Management (OPM), American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM), University of Georgia, Johns Hopkins University, and others.
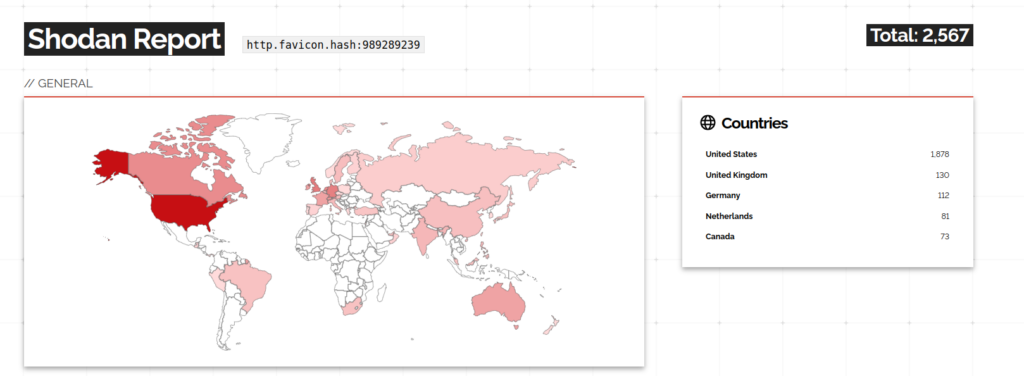
Any system using the MOVEit software that hasn’t patched the vulnerability is at risk. Particularly, if your infrastructure incorporates MOVEit for ‘Secure Managed File Transfer,’ it’s essential to take action. According to ‘IoT search engine’ Shodan Report, at least 2,500 networks are potentially exposed to the MOVEit vulnerability, the majority of which are located in the USA.
Recommended Actions Following MOVEit Exploitation
In response to the vulnerability, the provider has released some remediation steps and security recommendations, which are available on their community forum. But for a comprehensive approach to security, consider these security measures:
- Assess and Identify Necessary Services: By identifying services and applications that are essential for daily operations, it becomes possible to reduce the attack surface. Implement secure remote access protocols such as VPN or SDP, limit user access, and enhance authentication methods like multi-factor authentication.
- Implement Continuous Vulnerability Remediation: Regularly scan for vulnerabilities, patch them promptly, and ensure your systems are up-to-date.
- Deploy Multi-factor Authentication: Enhance your system’s security by requiring multi-factor authentication for all logins. This not only verifies user identities but also protects against unauthorized access.
- Monitor the Network Intentionally and Continuously: The truth will always be in the network. Regardless of any protection strategy in place, all organizations must develop the ability to detect threats in the network and make sense of them, as this gives them the ability to respond quickly and minimize the impact of attacks.
Beyond these steps, Lumu’s support can offer a last security layer, helping to assess your security posture and provide tools to correct it in time, as shown in our recent Davivienda case study.
Finally, always remember: a single vulnerability shouldn’t undermine your entire security strategy. Maintain a comprehensive cybersecurity approach that covers all bases, from robust identity access management to proactive vulnerability management. This will ensure resilience against the MOVEit vulnerability and many other zero-day vulnerabilities.