Table of Contents
Lumu’s annual Ransomware infographic, the 2023 Ransomware Flashcard, brings together stats and figures that give a snapshot of the state of ransomware in 2023. This infographic looks at how ransomware is evading defenses, how precursor malware is aiding in its spread, as well as its eventual cost and impact.
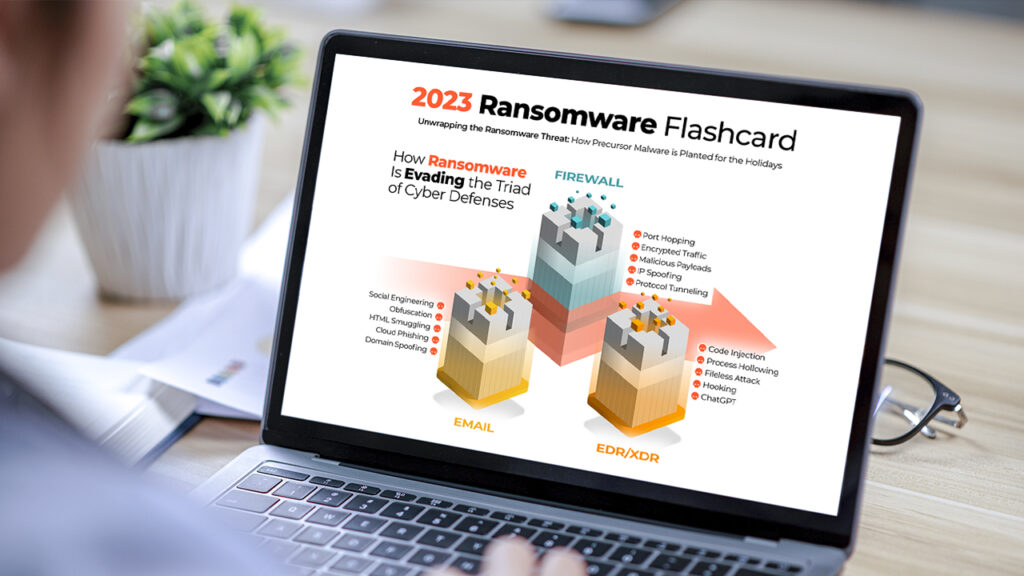
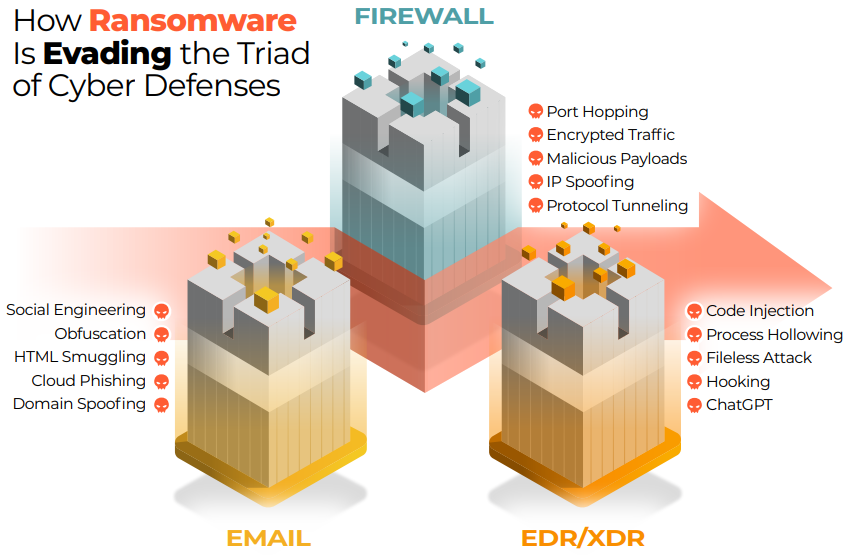
How Do Hackers Evade Cyber Defenses?
Our ransomware infographic first looks at how defenses are circumvented by hackers. Cybersecurity stacks vary according to the organization’s size, industry, budget, threat landscape, and several other factors, resulting in a complex array of in-house and outsourced cybersecurity tools and services. Nevertheless, the above triad of cybersecurity tools is fairly ubiquitous: email security, Endpoint Detection and Response, (including its trendier iteration Extended Detection and Response), and the Firewall.
While the list above is not exhaustive in terms of either tools or evasion techniques, it serves as a reminder that every cybersecurity tool in isolation can be bypassed by threat actors. A recent study found that almost all EDR and XDR solutions are vulnerable to at least one EDR evasion strategy. The lesson is that a defense-in-depth cybersecurity stack should be integrated and automated to close the gaps left by siloed cybersecurity tools.
What Are the Most Common Ransomware Precursors?
Before ransomware is deployed, hackers use precursor malware to gain access to the network, escalate privileges, and spread laterally.
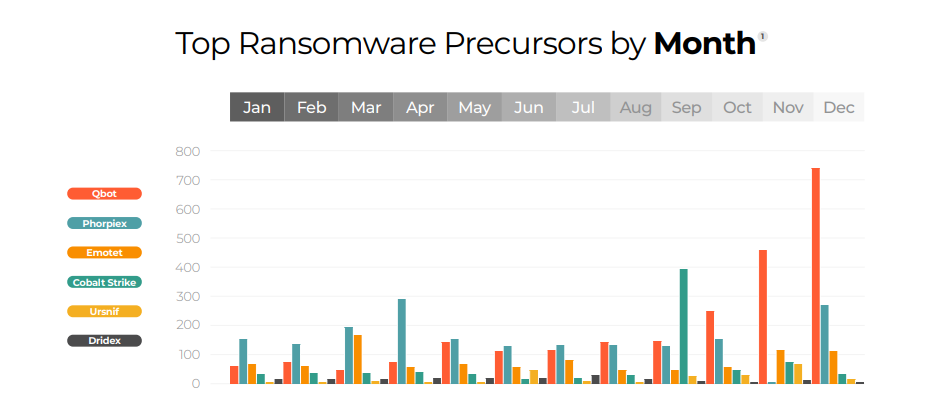
Lumu detected far more contacts from the following malware strains this year:
- Qbot: A versatile, modular botnet commonly spread through spam emails; it can steal banking credentials and execute other types of malware.
- Phorpiex: Another adaptable botnet often spread via spam emails; it has been used for sextortion campaigns and DDoS attacks.
Both of these strains are versatile, modular botnets, commonly spread through spam emails, and can be adapted to hackers’ needs. Interestingly, Lumu detected an increase in precursor malware activity in the months leading up to the holidays, showing that hackers are looking to lay the groundwork for attacks that they can launch when staff is on vacation.
What Is the Ultimate Impact of Ransomware?
Our ransomware infographic flashcard shows that the impact of ransomware continued to grow in 2023. In addition to the financial costs, organizations affected by ransomware may face:
- Reputational damage
- Operational disruptions
- Loss of sensitive data
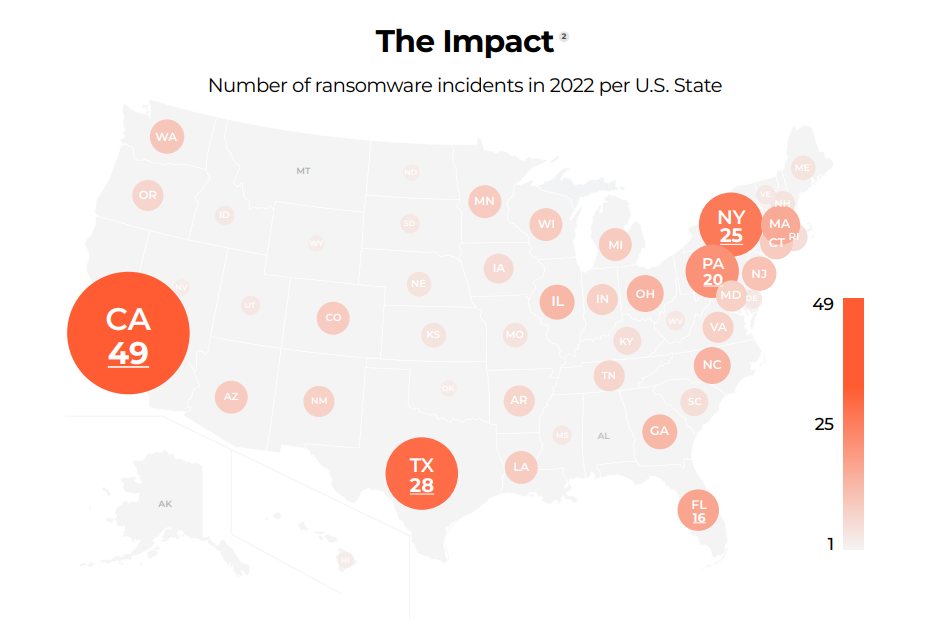
Nearly every U.S. state was affected by ransomware in some form. Wealthier and more populated states were more affected than others. Tech research firm Comparitech found a decrease in the number of ransomware attacks carried out in the USA throughout 2022. However, threat intelligence platform Darktracer saw an increase in 2022. The discrepancy in these findings reflects the difficulty in tracking and quantifying ransomware attacks accurately, as well as the evolving nature of cyber threats.
IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report found that the average cost of an individual ransomware attack increased from USD 4.62 Million to USD 5.12 Million.
For more at-a-glance stats and insights on the spread of Ransomware as well as additional information about specific evasion techniques and the consequences of attacks, be sure to access our freely available 2023 Ransomware Infographic Flashcard and in-depth report.